


Berthe Morisot, Woman Impressionist Marks Landmark Presentation
of the Artist’s Work in North America and France
of the Artist’s Work in North America and France

PHILADELPHIA– – The Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec (Québec City, Canada), the Barnes Foundation (Philadelphia, PA), the Dallas Museum of Art (Dallas, TX), and the Musée d’Orsay (Paris, France) announced the internationally touring exhibition dedicated to one of the revolutionary artists of the French Impressionist movement, Berthe Morisot (1841–1895). Co-organized by the four institutions, Berthe Morisot, Woman Impressionist will focus on the artist’s figure paintings and portraits through approximately 50 to 60 paintings from both public institutions and private collections. This tour will be the first dedicated presentation of Morisot’s work to be held in the United States since 1987, the very first solo exhibition of her work to be mounted in Canada, and the first time since 1941 that a French national museum will devote a monographic show to this important painter.
One of the founding members of the French Impressionists, Berthe Morisot was celebrated in her time as one of the leaders of the group, and her innovative works were coveted by dealers and collectors alike. Despite her accomplishments, today she is not as well-known as her Impressionist colleagues, such as Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, and Pierre-Auguste Renoir. Co-curated by Sylvie Patry, Chief Curator/Deputy Director for Curatorial Affairs and Collections at the Musée d’Orsay, Paris and Consulting Curator at the Barnes Foundation, and Nicole R. Myers, The Lillian and James H. Clark Curator of European Painting and Sculpture at the Dallas Museum of Art, Berthe Morisot, Woman Impressionist will both illuminate and reassert Morisot’s role as an essential figure within the Impressionist movement and the development of modern art in Paris in the second half of the 19th century.
The exhibition traces the exceptional path of a female painter who, in opposition to the norms of her time and social background, became an important member of the Parisian avant-garde from the late 1860s until her untimely death in 1895. Through her portrayal of the human figure, Morisot was able to explore the themes of modern life that came to define Impressionism, such as the intimacy of contemporary bourgeois living and leisure activities, the importance of female fashion and the toilette, and women’s domestic work, all while blurring the lines between interior and exterior, public and private, finished and unfinished.
Organized semi-chronologically, the exhibition will examine Morisot’s painterly innovations and fundamental position within Impressionism across the arc of her productive, yet relatively short life. The exhibition explores the following periods and themes of Morisot’s work:
- Becoming an Artist – The introductory section looks at Morisot’s formative years, when she left behind the amateur artistic practice associated with women of her upbringing and established herself as both a professional artist and a key contributor to the emerging Impressionist movement in the late 1860s and early 1870s.
- Painting the Figure en plein air – A selection of Morisot’s plein-air paintings of figures in both urban and coastal settings highlights her innovative treatment of modern themes and immersive approach that integrates her subjects within their environments through brushwork and palette.
- Fashion, Femininity, and la Parisienne – The importance of fashion in constructing modern bourgeois femininity forms a central part of the artist’s paintings of the 1870s and 1880s. This interest is revealed in Morisot’s creations and adaptations of quintessential Impressionist subjects, such as elegant Parisian women shown at the ball or dressing in their homes, and the leisure activities associated with suburban parks and gardens.
- Women at Work – Morisot’s depictions of the domestic servant—the majority of whom she employed in her household—reflect her own status as a working professional woman. Her interest in painting these women raises questions about bourgeois living and the intimacy of the shared domestic setting.
- Finished/Unfinished – The increasing immediacy of Morisot’s technique, and her radical experimentation with the concept of finished and unfinished in her work, exposes the process of painting and furthers the indeterminacy between figure and setting begun in her plein-air work.
- Windows and Thresholds – Morisot’s interest in liminal spaces is revealed in her paintings of subjects such as doorways and windows. Within these often spatially ambiguous settings, Morisot’s masterful evocation of light and atmosphere, the most ephemeral of her subjects, serves to anchor the human figure within these transitory spaces.
- A Studio of Her Own – Morisot’s late career paintings from the 1890s often depict her personal domestic space, which served as both studio and setting. During this period, Morisot reached a new expressiveness in her painting as figures become increasingly enveloped by their surroundings. The vibrant, saturated palette and sinuous brushwork that she adopted in these final works demonstrate their visual and symbolic affinities with the emerging Symbolist aesthetic of the time.
Exhibition Organization:
Berthe Morisot, Woman Impressionist is organized by Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec, the Barnes Foundation, the Dallas Museum of Art, and the Musées d’Orsay and de l’Orangerie. The exhibition is co-curated by Sylvie Patry, Chief Curator/Deputy Director for Curatorial Affairs and Collections at the Musée d’Orsay, Paris and Consulting Curator at the Barnes Foundation, and Nicole R. Myers, The Lillian and James H. Clark Curator of European Painting and Sculpture at the Dallas Museum of Art.
Berthe Morisot, Woman Impressionist is organized by Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec, the Barnes Foundation, the Dallas Museum of Art, and the Musées d’Orsay and de l’Orangerie. The exhibition is co-curated by Sylvie Patry, Chief Curator/Deputy Director for Curatorial Affairs and Collections at the Musée d’Orsay, Paris and Consulting Curator at the Barnes Foundation, and Nicole R. Myers, The Lillian and James H. Clark Curator of European Painting and Sculpture at the Dallas Museum of Art.
Exhibition Tour:
- Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec, Québec (June 21–September 23, 2018)
- The Barnes Foundation, Philadelphia (October 20, 2018–January 14, 2019)
- Dallas Museum of Art, Dallas (February 24–May 26, 2019)
- Musée d’Orsay, Paris (June 17–September 22, 2019)
Exhibition Catalogue:
The exhibition is accompanied by a fully illustrated catalogue that emphasizes the importance of understanding Morisot’s work in light of her dialogue with contemporary artistic movements—Impressionism, but also Post-Impressionism and Symbolism. Berthe Morisot, Woman Impressionist makes an important contribution to the field, with interdisciplinary scholarship and a specific focus on Morisot’s pioneering developments as a painter first, woman second. Edited by Sylvie Patry, an English- and French-language catalogue will be co-published by Rizzoli International Publications, Inc. and the Barnes Foundation, Philadelphia, in association with the Dallas Museum of Art and the Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec, Québec. A separate French-language catalogue will be published by the Musée d’Orsay, Paris. The book contains essays by Morisot scholars including the exhibition co-curators Sylvie Patry and Nicole R. Myers; Cindy Kang, Barnes Foundation; Marianne Mathieu, Musée Marmottan; and Bill Scott, Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts, as well as a chronology by Amy Wojciechowski with additional research by Monique Nonne (hardcover, $55).
The exhibition is accompanied by a fully illustrated catalogue that emphasizes the importance of understanding Morisot’s work in light of her dialogue with contemporary artistic movements—Impressionism, but also Post-Impressionism and Symbolism. Berthe Morisot, Woman Impressionist makes an important contribution to the field, with interdisciplinary scholarship and a specific focus on Morisot’s pioneering developments as a painter first, woman second. Edited by Sylvie Patry, an English- and French-language catalogue will be co-published by Rizzoli International Publications, Inc. and the Barnes Foundation, Philadelphia, in association with the Dallas Museum of Art and the Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec, Québec. A separate French-language catalogue will be published by the Musée d’Orsay, Paris. The book contains essays by Morisot scholars including the exhibition co-curators Sylvie Patry and Nicole R. Myers; Cindy Kang, Barnes Foundation; Marianne Mathieu, Musée Marmottan; and Bill Scott, Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts, as well as a chronology by Amy Wojciechowski with additional research by Monique Nonne (hardcover, $55).
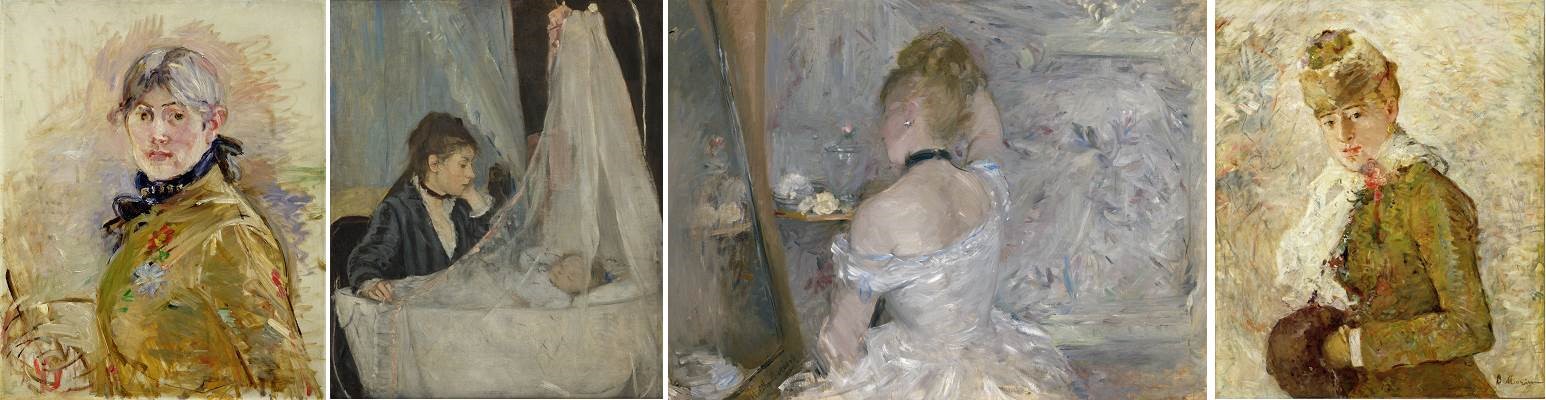
[Images (left to right): Berthe Morisot, Self-Portrait, 1885, oil on canvas. Musée Marmottan-Claude Monet, Fondation Denis et Annie Rouart, Photo courtesy Musée Marmottan Monet, Paris, France / Bridgeman Images; Berthe Morisot, The Cradle, 1872, oil on canvas, Musée d’Orsay, Paris, RF 2849, Photo by Michael Urtado. © RMN-Grand Palais / Art Resource, NY; Berthe Morisot, Woman at Her Toilette, 1875–1880, oil on canvas, The Art Institute of Chicago, Inv. no. 1924.127, Photo courtesy The Art Institute of Chicago / Art Resource, NY; Berthe Morisot, Winter, 1880, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, Gift of the Meadows Foundation, Incorporated, 1981.129]
About the Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec
Located in Québec City, the MNBAQ makes known, promotes and preserves Québec art from the 17th century to today with its rich collection of more than 38 000 works. The MNBAQ’s four pavilions are situated in the heart of the magnificent National Battlefields Park: the Gérard-Morisset pavilion (the original museum, 1933), the central pavilion (built in 1991), the Charles-Baillairgé pavilion (a prison dating from 1867), and the new Pierre Lassonde pavilion, giving the MNBAQ a street-front presence on one of the city’s main arteries, the Grande Allée. Designed by OMA New York in association with Provencher_Roy, this building enabled the MNBAQ to display its contemporary art, design, and Inuit art collections.
Located in Québec City, the MNBAQ makes known, promotes and preserves Québec art from the 17th century to today with its rich collection of more than 38 000 works. The MNBAQ’s four pavilions are situated in the heart of the magnificent National Battlefields Park: the Gérard-Morisset pavilion (the original museum, 1933), the central pavilion (built in 1991), the Charles-Baillairgé pavilion (a prison dating from 1867), and the new Pierre Lassonde pavilion, giving the MNBAQ a street-front presence on one of the city’s main arteries, the Grande Allée. Designed by OMA New York in association with Provencher_Roy, this building enabled the MNBAQ to display its contemporary art, design, and Inuit art collections.
About the Barnes Foundation
The Barnes Foundation is a nonprofit cultural and educational institution that shares its unparalleled art collection with the public, organizes special exhibitions, and presents programming that fosters new ways of thinking about human creativity. The Barnes collection is displayed in ensembles that integrate art and objects from across cultures and time periods, overturning traditional hierarchies and revealing universal elements of human expression. Home to one of the world’s finest collections of Impressionist, Post-Impressionist, and early modern paintings—including the largest groups of paintings by Pierre-Auguste Renoir and Paul Cézanne in existence—the Barnes brings together renowned masterworks by such artists as Henri Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Amedeo Modigliani, and Vincent van Gogh, alongside ancient, medieval, Renaissance, and non-Western art as well as metalwork, furniture, and decorative art.
The Barnes Foundation is a nonprofit cultural and educational institution that shares its unparalleled art collection with the public, organizes special exhibitions, and presents programming that fosters new ways of thinking about human creativity. The Barnes collection is displayed in ensembles that integrate art and objects from across cultures and time periods, overturning traditional hierarchies and revealing universal elements of human expression. Home to one of the world’s finest collections of Impressionist, Post-Impressionist, and early modern paintings—including the largest groups of paintings by Pierre-Auguste Renoir and Paul Cézanne in existence—the Barnes brings together renowned masterworks by such artists as Henri Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Amedeo Modigliani, and Vincent van Gogh, alongside ancient, medieval, Renaissance, and non-Western art as well as metalwork, furniture, and decorative art.
About the Dallas Museum of Art
Established in 1903, the Dallas Museum of Art (DMA) is among the 10 largest art museums in the country and is distinguished by its commitment to research, innovation and public engagement. At the heart of the Museum and its programs is its global collection, which encompasses more than 24,000 works and spans 5,000 years of history, representing a full range of world cultures. Since the Museum’s return to free general admission in 2013, the DMA has welcomed more than 3.2 million visitors. For more information, visit DMA.org. The Dallas Museum of Art is supported, in part, by the generosity of DMA Members and donors, the citizens of Dallas through the City of Dallas Office of Cultural Affairs, and the Texas Commission on the Arts.
Established in 1903, the Dallas Museum of Art (DMA) is among the 10 largest art museums in the country and is distinguished by its commitment to research, innovation and public engagement. At the heart of the Museum and its programs is its global collection, which encompasses more than 24,000 works and spans 5,000 years of history, representing a full range of world cultures. Since the Museum’s return to free general admission in 2013, the DMA has welcomed more than 3.2 million visitors. For more information, visit DMA.org. The Dallas Museum of Art is supported, in part, by the generosity of DMA Members and donors, the citizens of Dallas through the City of Dallas Office of Cultural Affairs, and the Texas Commission on the Arts.
About the Musée d’Orsay
Located in an old railway station opened in 1900 before being refurbished for its current purpose, the Musée d’Orsay has been renowned worldwide since its opening in December 1986. Devoted to the second half of the 19th century, it features collections of artwork primarily created between 1848 and 1914. All of the artistic movements of the time are represented: Impressionism, Realism, Naturalism, Post-Impressionism, Symbolism, etc., and the illustrious painters. Its multidisciplinary nature brings together all artistic fields: painting, sculpture, decorative art, objets d’art, architecture, drawing, and photography. Since June 1, 2010, the Musée de l’Orangerie has joined the Musée d’Orsay as part of one and the same publicly administered establishment.
Located in an old railway station opened in 1900 before being refurbished for its current purpose, the Musée d’Orsay has been renowned worldwide since its opening in December 1986. Devoted to the second half of the 19th century, it features collections of artwork primarily created between 1848 and 1914. All of the artistic movements of the time are represented: Impressionism, Realism, Naturalism, Post-Impressionism, Symbolism, etc., and the illustrious painters. Its multidisciplinary nature brings together all artistic fields: painting, sculpture, decorative art, objets d’art, architecture, drawing, and photography. Since June 1, 2010, the Musée de l’Orangerie has joined the Musée d’Orsay as part of one and the same publicly administered establishment.
No comments:
Post a Comment